AAST follows mandatry regulations and processes to prevent polluted water entering the water system, including pollution caused by accidents and incidents at the university as per the Egyptian governmental authority reguations. Wastewater is directed to a governmental treatment plant through a centralized sewage collection system found in all AAST campuses which is then connected to the public utility treatment company owned by each city. This framework is adopted across all public and private sector buildings in Egypt and is thus a compulsory act to ensure water is treated at national accepted levels and standards. Furthermore, AAST incorporates a waste management system that prevents pollution of water through several measures such as applying building standards that ensures compliance with the Egyptian Standard for Waste Disposal. This law establishes guidelines for safe and sustainable wastewater disposal to prevent contamination of watercourses. AAST implements a comprehensive waste management system across all campuses to ensure that wastewater is collected, treated, and safely disposed. In addition, AASTMT contineusly spreads awarness about wastewater treatment through different innetiatives and funded projects.
Responsible Consumption and Production-Alexandria | AASTMT
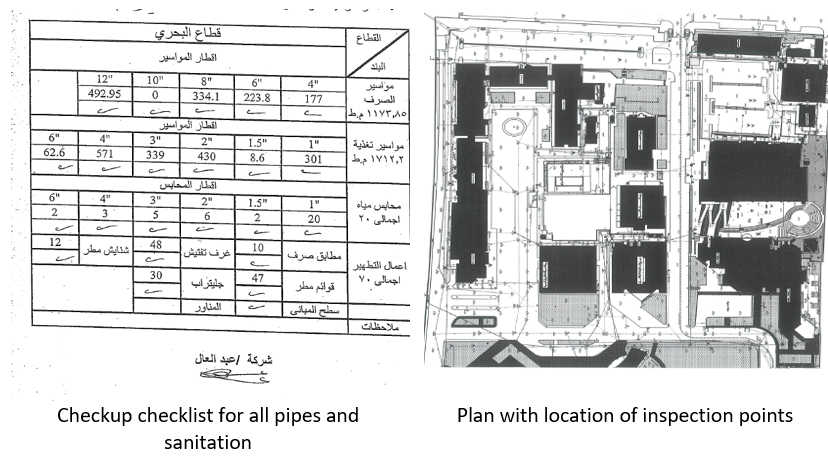
AASTMT’s drainage infrastructure demonstrates the institution’s commitment in preventing contamination, protecting groundwater, and ensuring safe wastewater management across campus facilities. The drainage system design for campus provides a clear model of how engineering systems can actively prevent pollution of water systems and ensure safe effluent conveyance and disposal through the following design strategies:
1. Pollution Control by Design:
2. Integration with Wastewater Treatment and Reuse:
3. Protecting Groundwater and Ecosystems:
4. Supporting Sanitation and Hygiene Goals:
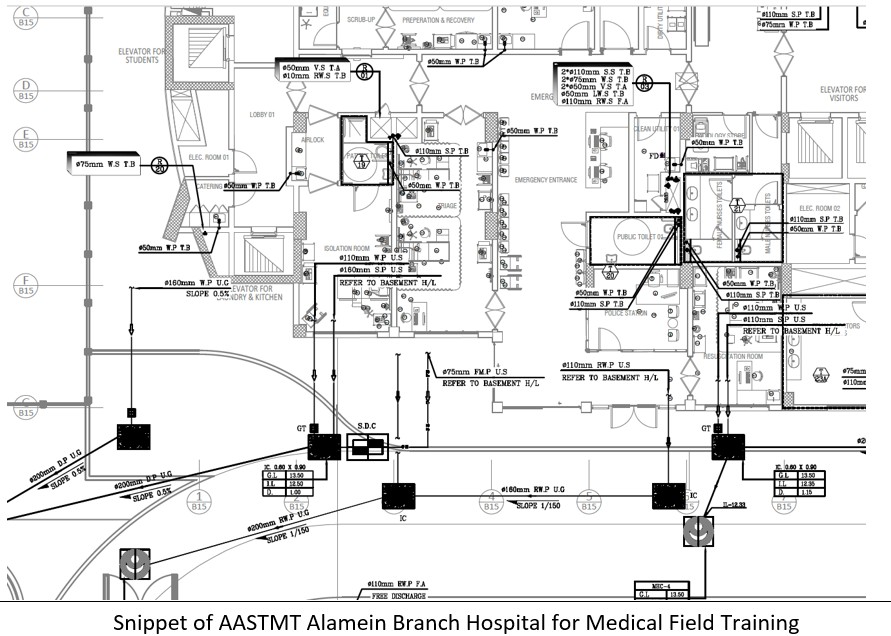
Incorporating a Framework for Safe Disposal of General Wastes through Shoots
In alignment with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, AASTMT – Alamein Branch has launched a comprehensive sustainable waste and water management system aimed at reducing pollution and protecting vital natural resources. This initiative introduces an efficient segregation and recycling system using stainless steel and color-coded bins to ensure proper collection, disposal, and resource recovery, minimizing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices. By preventing leachate and hazardous runoff, the system actively protects water quality, prevents contamination, and supports sustainable sanitation management, ensuring a cleaner and safer environment for the campus and surrounding communities. Through these integrated sustainability measures, AASTMT Alamein demonstrates leadership in environmental stewardship, contributing to Egypt’s Vision 2030 and serving as a model for green campus operations, where clean water, sustainable consumption, and environmental resilience are at the heart of institutional practice.
Incorporating a Framework for Safe Disposal of General Wastes through Shoots on AASTMT webpage
.png)
Incorporating a Framework to Ensure the Separation of Potable Water from Wastewater
The AAST follows all guidance measures as per the Code 102 Egyptian Code for the Design and Implementation of Drinking Water and Wastewater Networks (2010) to ensure the strict separation of drinking water and wastewater such as:
Code specifications can be found at
Incorporating a Framework to Ensure the Separation of Potable Water from Wastewater
Incorporating a Framework to Ensure the Separation of Potable Water from Wastewater
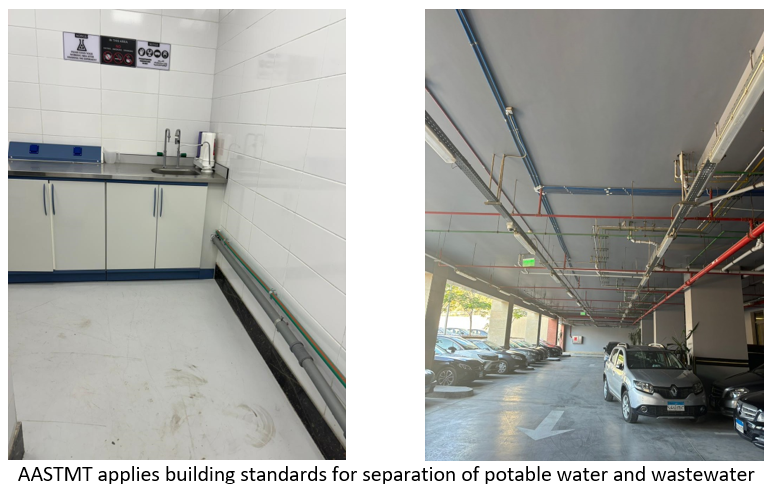
The plan below shows a section of one of AASTMT campuses. Red lines represent potable water while blue indicate wastewater. In addition, another picture shows two designated pipes inside AASTMT laboratories, where grey (larger diameter) used for drainage while sewage and green (smaller diameter) is for potable water or clean water supply that supply sinks and other fixtures.
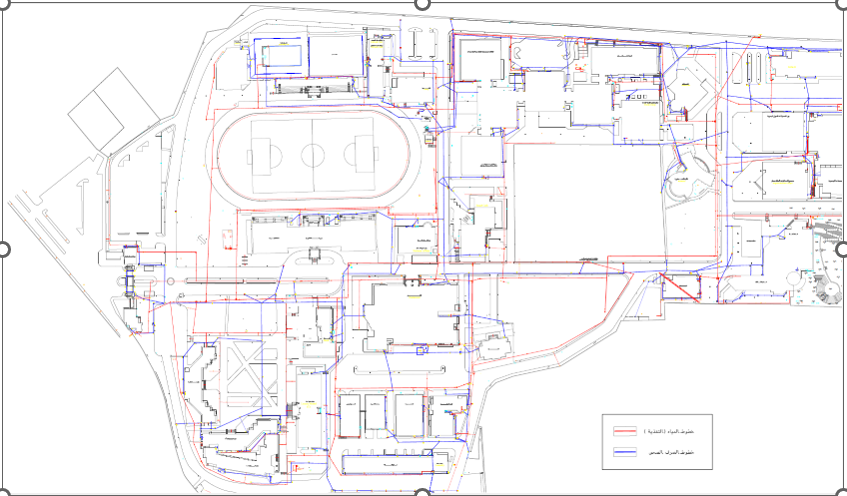

Incorporating a Framework for Managing Wastewater Discharge across Campus Facilities
Since the main water coming to all campuses arrives from the district governmental water company, the water gets filtered before entering the campus by district facilities. AASTMT relies on a water storage system in tanks specifically designated for drinking purposes, entirely separate from the sewage system. This strict separation ensures that the water reserved for drinking remains completely isolated from sewage water, upholding a stringent standard to assure the absolute safety and purity of the institution's potable water supply. Moreover, all clean water and wastewater systems in the buildings operate independently from each other. Wastewater systems are controlled and monitored via a designated control and monitoring system with redundant system operation, such that in the event of a failure, one panel will maintain functionality to prevent overflow or other discharge issues. The full function and operation of the wastewater discharge management can be found on:
Incorporating a Framework for Managing Wastewater Discharge across Campus Facilities on AASTMT webpage
In addition, AAST employs Operational Guidelines and Maintenance Standards as follows:
Emergency Protocols: the design of two electrical control panels manages pump operations and discharge flow, ensuring optimized, safe operations.

Incorporating a Framework for Safe Disposal of Wastes from Laboratories:
Safe disposal of laboratory waste targets the improvement of water quality by reducing pollution, through adherence to the Egyptian government waste disposal standards. Laboratory waste is collected, temporarily stored on campus, and scheduled for disposal twice a week. Certified disposal companies, adhering the Egyptian Law for disposal of hard materials number (6) for the year 2009 and number (9) for the year 1982 for governmental protection. AAST has a yearly contract with Nahdet Misr which manages the transport and disposal of these wastes into Alexandria Governorate Hazardous Waste Management (Naseria) for inorganic waste disposal. Proper handling and disposal of hazardous laboratory waste prevent harmful chemicals, biological contaminants, and pollutants from entering water sources. This is achieved by enforcing strict standards for containment, storage, transportation, and treatment of lab waste, ensuring it is neutralized or safely disposed of in certified facilities. In AASTMT separation of biological and chemical waste takes place inside AAST labs according to regulations set by Nahdet Misr. The company takes care of disposal of these substances at designated landfills at Naseria.
More information regarding the medical and biohazard disposal can be found in the following link:

.png)
.jpg)
.jpg)

Incorporating Waste Management System
AASTMT has implemented a comprehensive Recycling Policy to reduce its environmental impact and limit pollutant discharge into water sources.
The AAST addresses issues of potential water pollution by:
In 2022, the AASTMT continued safe disposal practices for toxic waste through Nahdet Misr for Modern Environmental Services, ensuring responsible collection, transportation, and treatment of medical and toxic waste to protect water supplies (Contracts and responsibilities can be found atAASTMT under “Waste Disposal Nahdet Masr Contract”. Laboratory waste is carefully categorized, with licensed contractors managing on-site packaging and handling based on waste type, ensuring compliance with necessary treatment methods.
Incorporating Waste Management System
Consumption and Recycling Policy
Water Usage & Care Practices
To reinforce these efforts, the AASTMT adheres to Environmental Standard ISO-14001, providing a systematic framework for managing environmental responsibilities.
Consumption and Recycling Policy on the AASTMT webpage
Life Policy on the AASTMT webpage
Water Usage & Care Practices on the AASTMT webpage
Consumption and Recycling Policy on AASTMT webpage
Water Usage & Care Practices on AASTMT webpage
Wastewater Treatment Workshops on AASTMT webpage
In addition, AASTMT spreads awareness and workshops with stakeholders for wastewater management as well as through scientific research.