
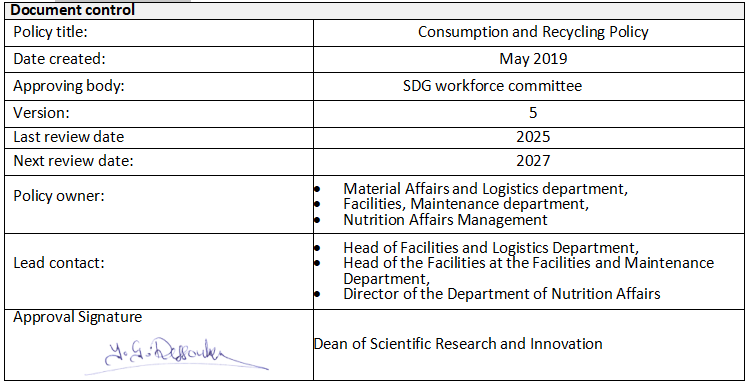
AASTMT is actively implementing innovative and sustainable waste management practices to minimize environmental impact and align with global sustainability standards. The institution emphasizes the importance of reducing reliance on traditional landfill disposal by adopting a comprehensive approach that prioritizes reducing, reusing, recycling, and recovering waste products. These initiatives not only minimize waste generation but also promote efficient resource utilization, encouraging practices such as material recovery and resource optimization. Through these efforts, AASTMT transforms waste management into an opportunity to create value while fostering a culture of environmental responsibility. By integrating environmentally friendly strategies into its operations, AASTMT reaffirms its commitment to sustainability, contributing to a cleaner, healthier environment for future generations and demonstrating leadership in environmental stewardship. Consumption and Recycling Policy is indicated in the following section and illustrated in point 4 under title “The Waste Treatment Progressive System and Stages Incorporates”, in addition at point number 6 under title action, it illustrate the future action that will be taken from AASTMT side.
1.Introduction
AASTMT recognizes the growing global challenges arising from the excessive pressure on natural resources, escalating greenhouse gas emissions, rising sea levels, pollution, and inefficient waste management. These environmental issues threaten both present and future generations, underscoring the urgent need for responsible consumption and effective recycling practices. In alignment with its Environmental Change and Social Responsibility Policy, AASTMT is committed to advancing the Sustainable Development Goals by promoting a culture of sustainability across all its campuses and operations. The Consumption and Recycling Policy reflects this commitment by emphasizing waste reduction, resource efficiency, and responsible material use.
Through this policy, AASTMT aims to minimize environmental impact by prioritizing waste prevention, reusing materials whenever possible, and ensuring proper recycling and disposal in compliance with environmental regulations. By fostering awareness and sustainable habits within its community, the University seeks to create a cleaner, safer, and more resilient environment for future generations.
2.Scope
This policy applies to all AASTMT employees, students, and contractors who are involved in handling, managing, or storing any form of waste, including hazardous and non-hazardous materials. It establishes the framework for ensuring that all waste management activities prioritize recycling, reuse, and responsible disposal in line with the university’s sustainability objectives.
Recycling must be integrated at every stage of the waste management process—beginning with proper segregation and collection, followed by safe processing and reuse wherever feasible. A designated responsible person or unit shall oversee the recycling and disposal of materials to ensure compliance with environmental standards and the adoption of the most sustainable methods available.
By embedding recycling practices into daily operations, this policy aims to minimize environmental impact, promote resource efficiency, and support AASTMT’s broader commitment to sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
3.Aims of the Policy
The AASTMT policy considers end-of-life disposal costs and environmental impacts when making acquisition decisions involving the construction of new or renovated facilities.
AASTMT receives the 'waste order' of Prevention, reuse, reusing, and other recuperation and removal. AASTMT executes cycles, methods, and activities that guarantee consistency with ecological enactment and best practice, to lessen the general waste produced and forestall waste creation at every possible opportunity. Moreover, AASTMT is committed to measuring and weighing the amount of waste generated to track the waste and to find the best methods to reduce or recycle it.
4.Procedures
The Waste Treatment Progressive System and Stages Incorporates:
Prevention
RE-USE
Recycle
Disposal
Ethical Sourcing of Food and Supplies
AASTMT is seeking to reduce food waste as much as we can through using food preservation methods and vermicomposting practices. The university is committed to delivering healthy food for all parties in the university including food on Campus, Residences, and employees whether vegetarian or others. AASTMT makes sure that the food is available at each level to guarantee healthy food for ASTMT’s stakeholders. However, food waste is still a problem for AASTMT. Therefore, AASTMT is applying the following procedures to use the waste of food in an appropriate way:
5.Policy Statement
The AASTMT seeks to implement ethical and sustainable practices on all of its campuses. Therefore, the AASTMT has taken crucial measures to implement these practices, such as ecological practices and corporate social responsibility. Through the exchange of information within the Academy's supply chain, these food ethics and practices enable AASTMT to ensure the transparency of information about all suppliers.
To accomplish supply chain transparency, one of the primary goals of AASTMT is to identify the most reliable and reputable partners who share the same ethical practices, objectives, and data. To accomplish ethical and sustainable practices, the first step is to identify the most suitable suppliers.
The interaction with suppliers is the second step to keep secure relationships between partners and to reduce the risk. AASTMT is seeking to build a platform and application to increase communication and share important information. That would give the suppliers and partners access to the internal systems they need based on their roles within the ecosystem, sustainability practices, and the food ethics of AASTMT.
Through utilizing new technologies such as block chain technology, AASTMT plays a crucial role in facilitating the monitoring and tracing of the origin of food. It allows the AASTMT to trace the origin of food and ensure its safe delivery to campuses.
AASTMT is monitoring the overall processes between its partners to guarantee healthy and sustainable food for students, staff, and Residents. Based on this monitoring, errors must be fixed, and corrective action must be taken.
AASTMT guarantees that we are conforming to guidelines, enactment, and best practices to limit the danger of prompt and future contamination or mischief to wellbeing when completing operational exercises.
6.Actions
7.Objectives:
Waste ought to be forestalled or limited at every possible opportunity. AASTMT empowers staff, Students, and employers to limit plastic and cartoon waste, in addition to increasing the awareness about the method to minimize disposable items.
8.Review Program

You can read our Consumption and Recycling Policy on AASTMT website.
More activities are applied and practiced in the AASTMT.
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) delivers 23 sanitary landfills for waste management across 16 governorates.
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) announced that it has been working on developing Egypt’s Solid Waste Management System over a four-year period (2019–2023). The Academy stated that it collaborated with the relevant ministries to establish the infrastructure for the new waste management system and trained and qualified personnel across Egypt’s governorates to operate, manage, and monitor the system at all stages from collection and transportation to treatment and safe disposal of waste.
In its statement, AASTMT added that it has played a pivotal role in localizing international systems and modern technologies in the field of waste management. The Academy has raised awareness among decision-makers in various governmental entities about global best practices for managing different types of waste household, agricultural, industrial, and hazardous with the aim of guiding Egypt’s national plans toward optimal integrated waste management and maximizing the economic return on government investments in this sector.
AASTMT Participates in the Handover of Juhayna Sanitary Landfill in Sohag Governorate
The Ministries of Environment and Local Development have officially handed over the sanitary landfill in Juhayna, Sohag Governorate, with a total investment of approximately EGP 60 million. The project was delivered through a specialized committee comprising representatives from the Ministry of Environment, Ministry of Local Development, Ministry of Defense (represented by the Military Technical College and the Arab Organization for Industrialization), and the Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT). This committee is responsible for supervising, monitoring, and receiving infrastructure projects under the first phase of the national Integrated Solid Waste Management Program, ensuring full compliance with all contract terms. The landfill, established on 10 acres, serves the districts of Juhayna and Al-Maragha, and includes a 30,000 m² disposal cell, administrative buildings, fuel and water tanks, and environmental safety measures designed to ensure secure and sustainable waste disposal in line with Egypt’s national waste management strategy.

AASTMT Involved in Beni Suef Landfill Handover
AASTMT Abu Qir Campus Hosts Seminar on Recycling Straw Waste for Sustainable Industrial Innovation
As part of its commitment to fostering well-rounded students with strong scientific and cultural awareness, the Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT), through the Institute of Basic and Applied Sciences under the leadership of Prof. Nasser Mohamed El-Maghraby and the patronage of Prof. Akram Suleiman El-Selmy, Dean of the College of Engineering and Technology – Abu Qir Campus, will host a seminar titled “Recycling of Straw Wastes to MDF ECO-Boards: Towards an Urban Environment.” The event, featuring Eng. Walid Shafik, Head of Operations at WOTECH Egypt, will be held on Tuesday, October 21, 2025, in Al-Farsi Hall, and aims to educate students on the economic, environmental, and technological importance of waste recycling in industry. The seminar is organized by Prof. Allam Abdelaziz, Dr. Sherif Zafar El-Degani, Dr. Engy Ibrahim, and Dr. Baraa Adel, reflecting AASTMT’s dedication to linking academic knowledge with practical industrial sustainability.

AASTMT Seminar on Straw Waste Recycling
AASTMT Showcases Innovative Spin-Offs Driving Sustainability, Health, and Smart Technology across Egypt
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) has launched and supported a diverse portfolio of entrepreneurial spin-offs that reflect its strong commitment to innovation, sustainability, and social impact. Among these ventures are HELFEX Robotics, which develops rehabilitation exoskeletons for children with mobility disabilities; Carbocycle, focusing on solar-powered clean energy solutions for agriculture; ReNile, providing IoT-based smart farming and environmental monitoring systems; and Aqua Valley, which recycles and reuses fish farm water for organic irrigation. Other notable companies such as Biomass, SH-N Formulation, and Kadry Group contribute to waste recycling, green energy production, and sustainable food systems. Through these initiatives, AASTMT continues to empower innovators, promote circular economy practices, and strengthen Egypt’s position as a regional leader in sustainable technological development.
AASTMT Spin-Offs Promote Innovation and Sustainability
AASTMT Spin-Offs Promote Innovation and Sustainability
AASTMT Participates in National Conference on Sustainable Industry and Water Management in Alexandria
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) participated in the National Conference on the Sustainability of the Water and Wastewater Industry, held under the patronage of the Ministry of Housing, Utilities and Urban Communities, the European Union Delegation in Cairo, and the Alexandria Governorate. The event, also supported by several national and private-sector organizations, aimed to advance Egypt’s Vision 2030 by promoting sustainable industrial practices, localizing water and wastewater technologies, and encouraging public-private partnerships. AASTMT’s involvement underscores its continued commitment to fostering sustainable water management, infrastructure development, and climate resilience—particularly in Alexandria, a coastal city facing increasing climate change challenges.

AASTMT Joins Sustainability Conference in Alexandria
AASTMT Participates in National Conference on Sustainable Industry in Water and Wastewater Services
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) participated as a key partner in the National Conference on the Sustainability of the Water and Wastewater Industry, held in Alexandria under the patronage of the Ministry of Housing, the European Union Delegation in Cairo, and the Alexandria Governorate. The event brought together national and international experts to discuss innovative solutions for sustainable water and wastewater management, infrastructure development, and industrial localization in alignment with Egypt’s Vision 2030. AASTMT’s involvement highlights its continued efforts to bridge academia, industry, and government in promoting environmental sustainability and supporting Egypt’s strategic initiatives toward integrated resource management and climate resilience.

AASTMT Joins Water Sustainability Conference in Alexandria
AASTMT Strengthens Cooperation with Alexandria Sanitation Company for Scientific and Technical Development
The Arab Academy for Science, Technology and Maritime Transport (AASTMT) President, Dr. Ismail Abdel Ghaffar, met with Eng. Mahmoud Nafea, Chairman of the Alexandria Sanitation Company, to discuss expanding cooperation in the fields of laboratory development, scientific and technical training, and research unit support. The meeting emphasized implementing the recommendations of the National Conference on the Sustainability of Water and Wastewater Industry, co-organized by AASTMT earlier this year, aiming to localize industrial and environmental technologies to address wastewater pollution challenges. Both parties agreed to advance research collaboration, promote institutional excellence, and integrate smart technologies to enhance operational performance and ensure sustainable water and sanitation services in Alexandria.